Common Misconceptions About Mute People
Mute people aren't deaf, limited in intelligence, or emotionless, they communicate richly via sign, text, and tech. Bust 10 myths with medical facts.
Editorial Team
Direct Answer
Mute individuals are often misunderstood due to the visible nature of their silence. Contrary to popular belief, most mute people can hear perfectly, feel emotions as deeply as anyone else, and possess average or above-average intelligence. Mutism is a communication barrier, not a cognitive or auditory one.
Medical Background on Myths
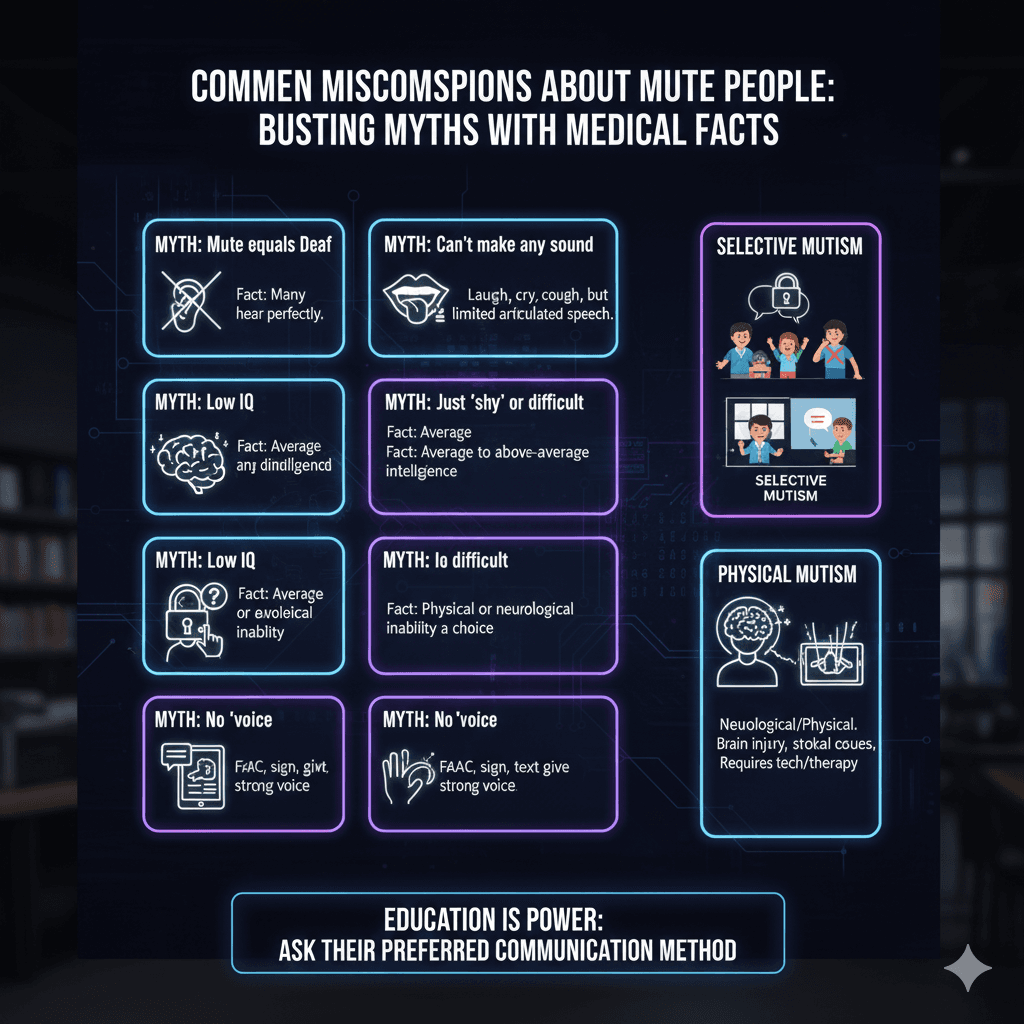
It is crucial to distinguish between types of mutism. Selective Mutism is an anxiety-based condition where a person is physically able to speak but 'freezes' in specific social settings. Physical Mutism involves the vocal cords or brain injuries (like aphasia). Neither condition impacts a person's ability to understand tone, logic, or emotion.
Top Misconceptions Busted
- Myth: Mute equals Deaf. Fact: They are separate conditions. Many mute people have perfect hearing.
- Myth: They can't make any sound. Fact: Many can still laugh, cry, or cough; the limitation is usually on articulated speech.
- Myth: Mutism is a sign of low IQ. Fact: There is no correlation between speech and intelligence.
- Myth: They are just being 'difficult' or 'shy'. Fact: Mutism is often a physical or neurological inability to produce speech at that moment.
- Myth: They have no 'voice'. Fact: Through AAC, sign language, and text, their voice is as strong as anyone's.
Real Impact & Education
These myths often lead to social isolation. Education is the first step toward inclusion. When you meet a mute person, don't assume they can't hear you, simply ask for their preferred communication method (text, sign, or app).
FAQs
- Can therapy 'cure' mutism? For selective mutism, CBT and shaping techniques are highly effective. For physical mutism, it depends on the underlying medical cause.
Link: Understanding different types of mutism. References: Mayo Clinic | Myths & Facts About Disability


